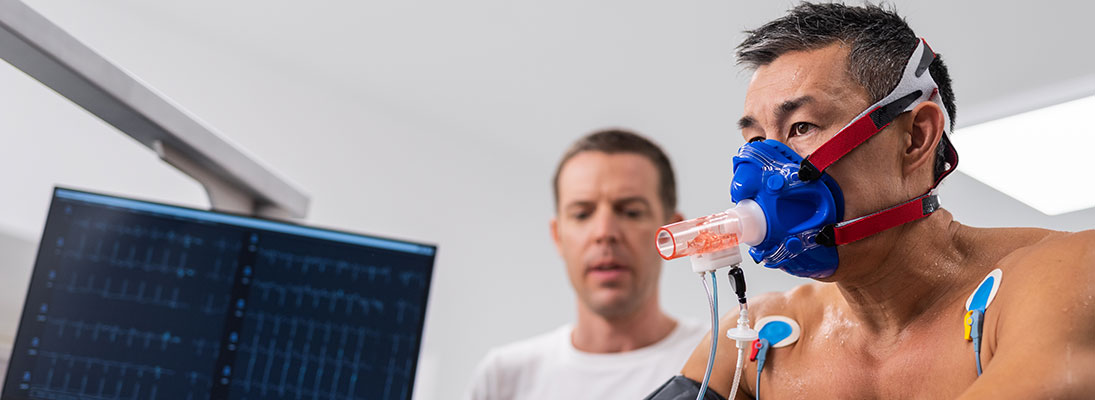

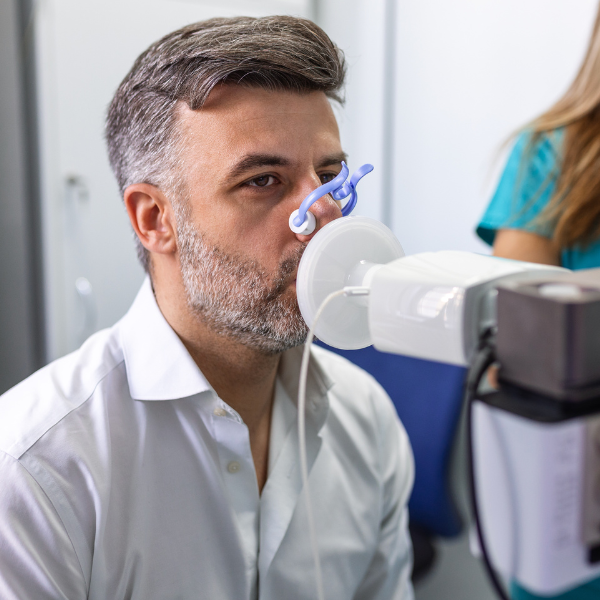
If spirometry and inhaling bronchodilators can't show if you have asthma, your healthcare provider may ask you to take an exercise challenge test. This test shows if you have exercise-induced asthma or bronchoconstriction (narrowing of the airways that carry air in and out of the lungs).
How Does the Exercise Challenge Test Work?
You’ll begin with a spirometry test to measure how much air you can inhale and quickly exhale. You'll then exercise for a short amount of time on either a treadmill or stationary bike, while you breathe in cool and dry air. The spirometry test will then be repeated a few more times to measure your lungs’ response.
How to Prepare for Your Test
For this test, it’s important that you:
Shave off any chest hair before your appointment
Avoid heavy exercise four hours prior to the test
Do not eat a heavy meal three hours before the test
Do not smoke three hours before the test
Do not consume alcohol three hours before the test
Your appointment may be rescheduled if you haven’t prepared according to these criteria.
Call us ahead of time if you:
Have an inability to follow instructions*
Have had a heart attack in the past month
Have uncontrolled hypertension
Are pregnant
Are currently using cholinesterase inhibitor medication (e.g. myasthenia gravis)
Have chest or abdominal pain
Have excessive pain while using a mouthpiece
Have had recent eye surgery (1 week to 6 months, depending on type of surgery)
Have had recent brain surgery or injury (3 to 6 weeks)
Have had a collapsed lung (2 weeks)
Are spitting up blood
*If a patient is unable to follow instructions due to a confused state, young age or dementia, then a parent, caregiver or guardian may call on their behalf.
Medications to Withhold Before Your Appointment
Do not take any of the following medications during the window of time outlined before your appointment:
Inhaled beta-agonists in conventional doses
Short-acting (e.g. albuterol): 6 hours
Long-acting (e.g. salmeterol): 36 hours
Inhaled anticholinergics
Short-acting (e.g. ipratropium): 12 hours
Long-acting (e.g. tiotropium): 48 hours
Antihistamines
Short-acting (e.g. Benadryl): 48 hours
Long-acting (e.g. Allegra): 72 hours
Need More Information?
Download additional information on your test procedure.
If you have any questions about your test, please call us:
Adult Testing
Pediatric Testing
We use cookies and other tools to optimize and enhance your experience on our website. View our Privacy Policy.
